Bcdedit set pciexpress forcedisable что это
Видеокарта AMD или NVIDIA не обнаружена в Windows 10
Графическая карта — это компьютерное оборудование, которое отвечает за отображение изображения, которое вы видите на экране вашего компьютера. Это отличный способ установить соединение между монитором и компьютером.
Однако иногда вы можете столкнуться с проблемами с графическим драйвером AMD или NVIDIA. В такие моменты ваша система Windows 10 не обнаруживает вашу NVIDIA или видеокарту AMD. Вы можете увидеть сообщения об ошибках, такие как:
Если видеокарта AMD или NVIDIA не обнаружена в вашей системе Windows 10
Выполните следующие рекомендации чтобы обнаружить видеокарту:
1] Перезапуск видеокарты
Эта проблема обычно возникает, если графическая карта отключена в диспетчере устройств. Так что, в таком случае, включение видеокарты было бы хорошей отправной точкой. Вот краткое руководство:
После этого перезагрузите компьютер и проверьте решена ли проблема. Т.е вам необходимо отключить и включить видеокарту или в обратном порядке, если она была отключена.
2] Используйте командную строку
Откройте командную строку с правами администратора, введите следующую команду и нажмите Enter:
После выполнения команды, закройте окно и перезагрузите пк и проверьте решена ли проблема. Если нет, приступите к слудующему шагу если драйвера не обнаруживают видеокарту.
3] Установите последние версии графических драйверов
В случае, если ни один из описанных выше способов не работает для вас, вам необходимо загрузить последние версии драйверов NVIDIA для вашего компьютера.
Прежде чем начать, сначала необходимо удалить все предыдущие драйверы NVIDIA, установленные на вашем устройстве.
Для этого откройте «Настройки Windows» (Win + I) и выберите категорию «Приложения».
В разделе «Приложения и Возможности» прокрутите колесо мыши и найдите драйверы, связанные с NVIDIA или AMD.
Теперь выберите их по одному, а затем нажмите кнопку «Удалить».
Затем следуйте инструкциям на экране для завершения процесса удаления.
Устранение проблем с отображением видеокарты в Windows 10
Способ 1: Обновление ПО устройств
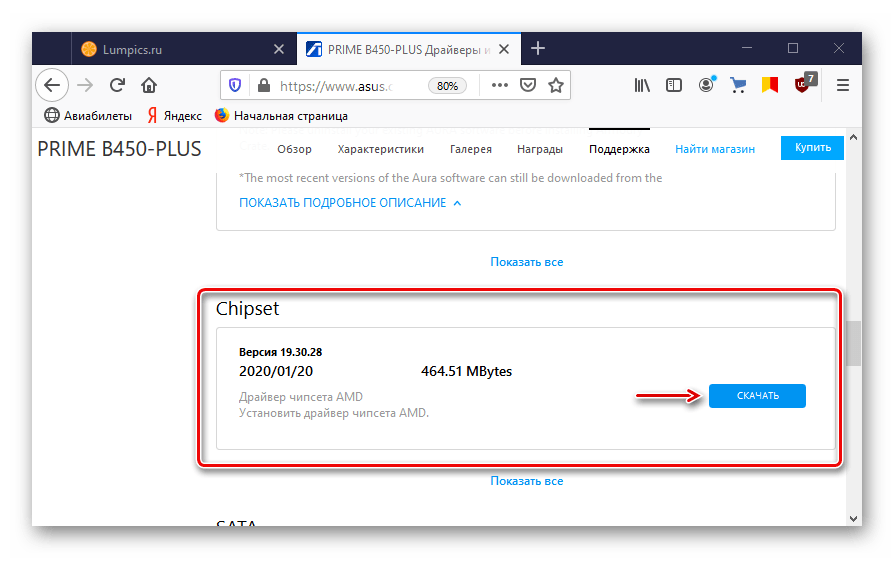
Обычно описанная проблема связана с драйверами. Они либо вообще не установлены, либо загружены из сторонних источников. В любом случае, чтобы система поняла, с каким оборудованием и как ей работать, нужны оригинальные драйверы. Сначала скачиваем ПО для материнской платы, берем файлы с официального сайта. Нас интересует чипсет и VGA-драйвер, если плата с интегрированным видео. Если поддержка оборудования уже закончилась, загружаем самую последнюю их версию. О том, как установить драйверы материнской платы, написано в отдельной статье.
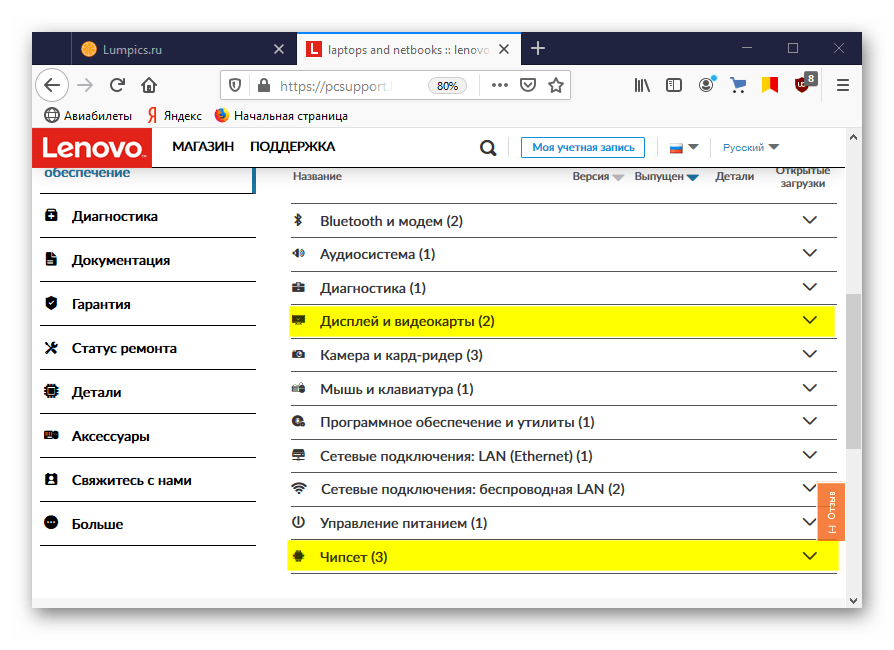
Большинство ноутбуков оснащено двумя видеокартами, поэтому также скачиваем ПО для чипсета и встроенного графического процессора. Подробную инструкцию по обновлению драйверов на примере ноутбука Lenovo вы найдете на нашем сайте.
Видеодрайверы для дискретной графической платы загружаем с официального сайта ее производителя. Если они уже установлены, но система все равно не видит устройство, сделайте чистую установку с удалением старого ПО, например, с помощью утилиты DDU. О способах обновления драйверов видеокарты и удаления уже установленных мы подробно писали в отдельных статьях.
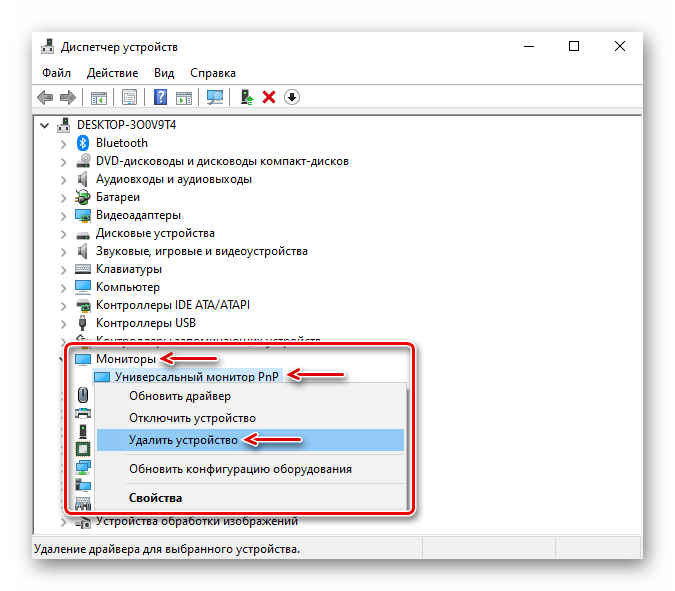
Дополнительно перед установкой программного обеспечения попробуйте удалить мониторы из соответствующей вкладки в «Диспетчере устройств». Некоторым пользователям это помогло.
Способ 2: Отладка драйвера шины PCI
В Виндовс 10 есть встроенное хранилище данных конфигурации загрузки (BCD). В нем параметры, которые используются при настройке и загрузке операционной системы, а также других загружаемых программ и устройств. Для создания новых конфигураций загрузки системы, а также тестирования и отладки драйверов на компьютерах под управлением Windows параметры можно менять при помощи встроенной утилиты BCDEdit.
Например, таким образом можно устранить неполадки с драйверами шины PCI Express на материнской плате, которая используются для подключения видеокарты. В данном случае нам понадобится команда, которая отключает и включает функцию PCI Express, а также дополнительное к ней значение, которое переопределяет ее расширенные опции и возвращает рабочее поведение.
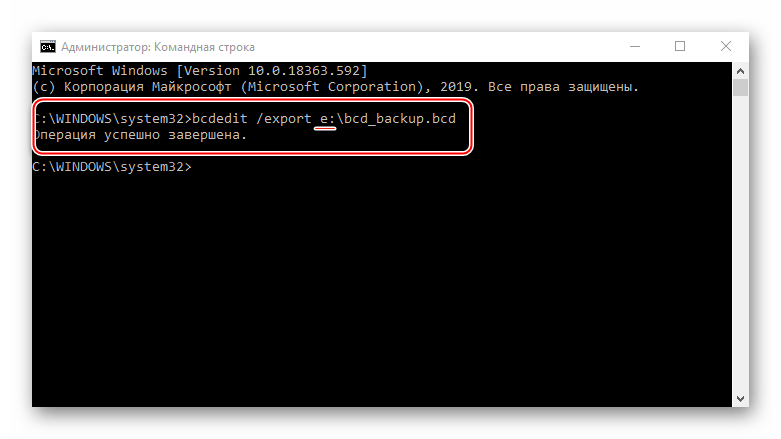
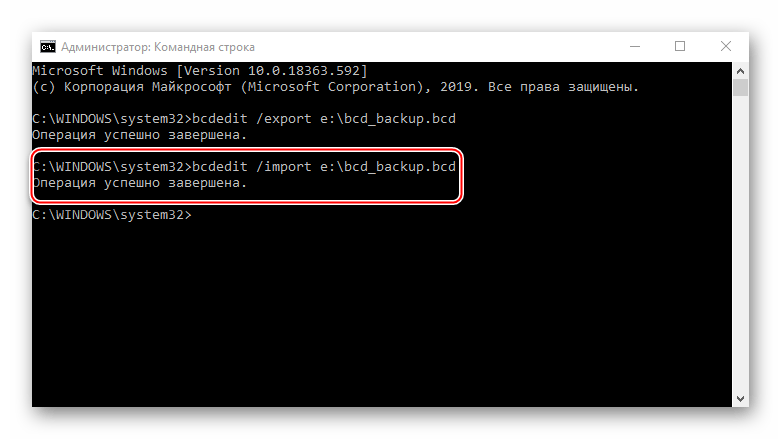
bcdedit /export e:\bcd_backup.bcd
где буква е – это любой диск, на котором будет храниться резервная копия, а «bcd_backup» — любое название копии.
Файл будет лежать в корневом разделе диска.
bcdedit /import e:\bcd_backup.bcd
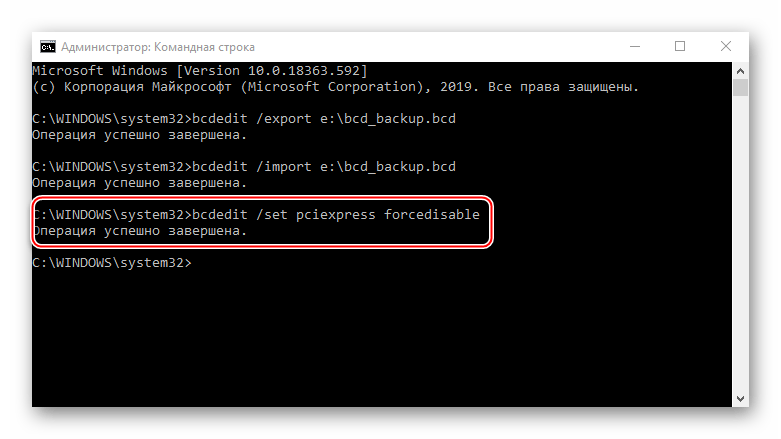
bcdedit /set pciexpress forcedisable
нажимаем «Enter». Перезагружаем компьютер и пробуем установить драйверы.
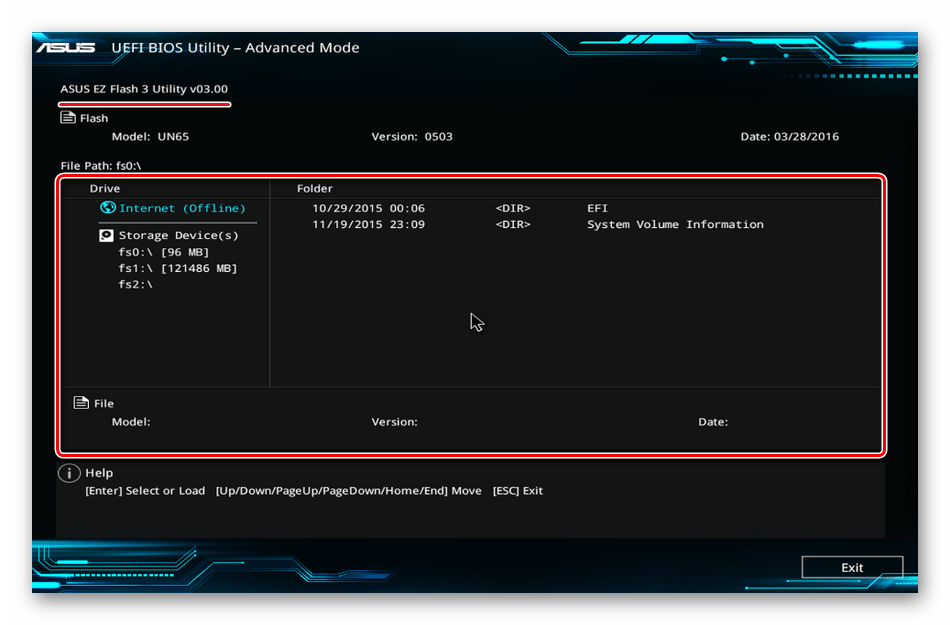
Способ 3: Настройка BIOS (UEFI)
BIOS материнских плат со встроенным графическим ядром обычно оснащают функцией переключения видеокарт. Она может пригодиться, если, например, вы купили дискретную графическую карту, вставили ее в слот PCI Express, подключили к монитору, включили компьютер, а изображения на экране нет, хотя слышно, что система загрузилась. Это может значить, что соответствующий слот отключен на уровне BIOS (UEFI). На многих ноутбуках такая возможность тоже есть. Воспользуйтесь ей, если одна из видеокарт не определяется системой.
Наименование функции переключения графики и включения слотов в разных BIOS может отличаться. Информацию об этом, а также о наличии опции нужно уточнять в руководстве по эксплуатации материнской платы или ноутбука.
Перед тем как настраивать BIOS проверьте наличие обновлений для него. При стабильной работе компьютера это делать не рекомендуется, но учитывая возможный конфликт с оборудованием, есть шанс, что с новой версией микропрограммы проблема решится. Как в общих чертах выглядит процесс обновления BIOS (UEFI), мы подробно описали в другой статье.
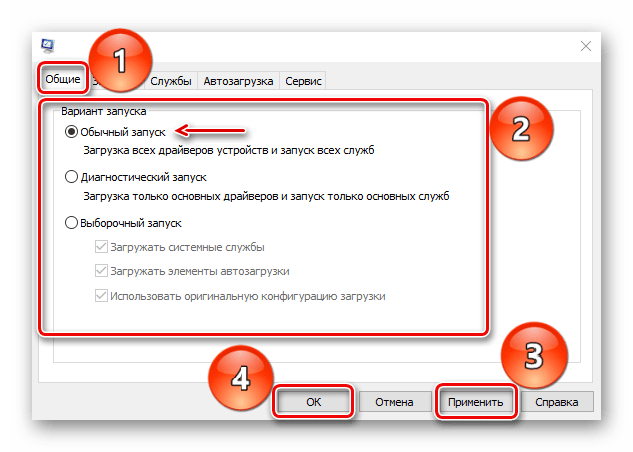
Способ 4: Изменение типа запуска Windows
Многие неполадки в работе системы и оборудования можно устранить с помощью встроенной утилиты Msconfig, предназначенной для управления загрузкой Виндовс. Она поддерживает три варианта запуска: обычный, диагностический и выборочный. Нас интересует обычная загрузка с запуском всех служб и драйверов всех устройств.
Способ 5: Проверка оборудования
Проверьте комплектующие, связанные с видеокартой. Уточните мощность блока питания. Возможно, ее не хватает для нормальной работы устройства. В этом случае проблему решит покупка нового БП. Проверьте, правильно ли подсоединено дополнительное питание. Выньте карту, удалите с нее пыль и аккуратно зачистите контакты ластиком.
Если позволяет конструкция материнской платы, поменяйте слот или по возможности подключите к ней заведомо рабочую видеокарту. Можно, наоборот, подсоединить графическую плату к другому компьютеру. Эти действия помогут понять, неисправен сам видеоадаптер или дело в другом оборудовании.
Надеемся, описанные способы помогли системе увидеть видеокарту. Если проблема осталась, изучите мануал к устройству, а также ознакомьтесь с информацией о нем на сайте производителя. Возможно, графическая плата была разработана намного раньше выхода Windows 10 и не соответствует ее минимальным требованиям, а значит, есть вероятность, что система ее не определит.
Помимо этой статьи, на сайте еще 12483 инструкций.
Добавьте сайт Lumpics.ru в закладки (CTRL+D) и мы точно еще пригодимся вам.
Отблагодарите автора, поделитесь статьей в социальных сетях.
Почему компьютер не видит видеокарту: 12 советов, что делать если ПК или ноутбук не видят видеоадаптер

Придется выяснять, почему не определяется видеокарта в Windows. С помощью собранного специально по этой теме материалу мы постараемся помочь в решении возникшей проблемы. Мы также советуем ознакомиться со статьями, как проверить видеокарту, и как переключить видеокарту на ноутбуке, возможно они будут полезны.
Существует две различных проблемы видимости видеокарты
Обнаружить наличие неисправности в отношениях между компьютером и видеокартой (графическим процессором) можно, столкнувшись с двумя ситуациями:
Проявиться проблема может в нескольких ситуациях:
Если у вас возникли проблемы с использованием видеокарты, предлагаем ознакомиться с предложенными вариантами решения. Они помогут вернуть оборудованию работоспособность, не зависимо от того, устанавливали вы новую плату или проблема возникла на старом оборудовании.
11 способов заставить компьютер видеть видеокарту
Среди предложенных ниже решений есть как программные методы, так и аппаратные, которые помогут компьютеру распознать видеокарту, если система не выявила ошибки для AMD или Nvidia.
Совет #1: Некоторые ноутбуки имеют кнопку включения дискретной видеокарты
Многие ноутбуки оснащены отдельной физической кнопкой включения дискретной видеокарты. В диспетчере устройств на таких ноутбуках даже может не отображаться дискретная видеокарта. Это нормально. Поэтому, в первую очередь советуем поискать кнопку включения дискретного видео. Часто она обозначается как GPU.
Совет #2: Попробуйте установить видеокарту в ПК заново
Чтобы выяснить, виновато ли качество соединения в том, что не включается видеокарта на компьютере, нужно заглянуть в системный блок. Обесточьте компьютер и снимите боковую крышку, чтобы получить доступ к его внутренне части. Обратите внимание на слот PCI-Express x16 – насколько плотно прилегают контакты. Рекомендуем осторожно вынуть видеокарту из слота и вставить ее заново, убедившись, что контакты вошли до конца. После чего можно включать компьютер и проверять работоспособность оборудования. Если неисправность не исчезла – пробуйте следующий шаг.
Совет #3: Проверьте, не отключена ли видеокарта в настройках BIOS
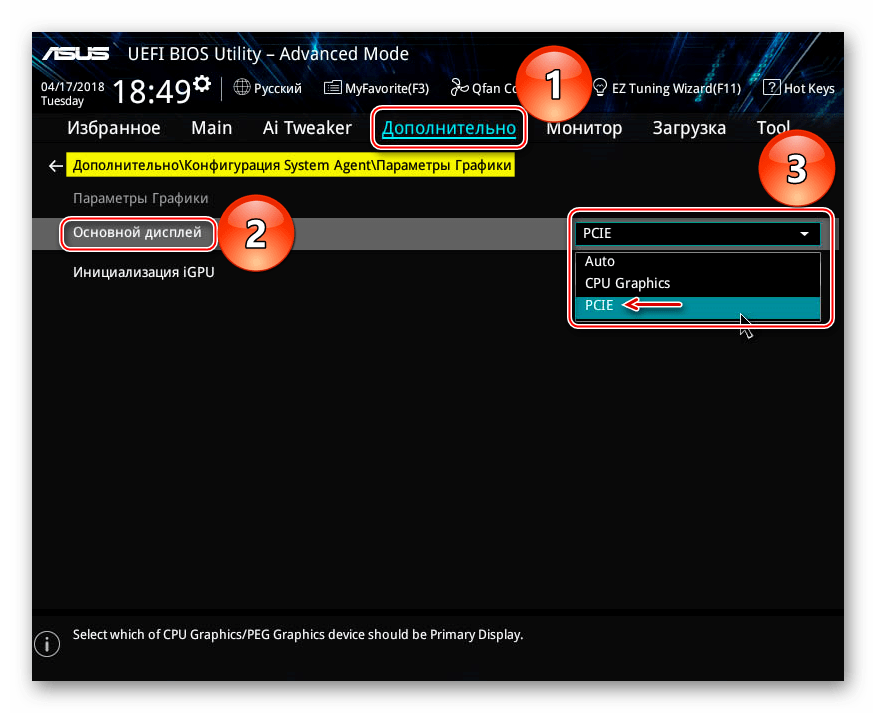
Причина, по которой компьютер или ноутбук не видит видеокарту nVidia или AMD Radeon может крыться в настройках BIOS. Особенно часто это возникает, когда комп уже имеет интегрированный аналог, и обращается по умолчанию к нему, а не к выделенной графике. На разных моделях наименования разделов системы может отличаться, но основная суть одна – установить нужный параметр для PCI-Express Graphics.
При подключении дискретной графики важно указать компьютеру на то, что она для него должна быть в приоритете. Тогда система перестанет обращаться к встроенному аналогу и начнет работать с новым устройством. Сделать это легко в BIOS, выставив правильные значения:
Теперь сохраните все внесенные изменения, чтобы после перезарузки компьютера они вступили в силу и дали положительный результат. Поэтому перед перезапуском, зайдите на вкладку «Exit» и нажмите «F10».
Совет #4: Проверьте, включена ли видеокарта в диспетчере устройств
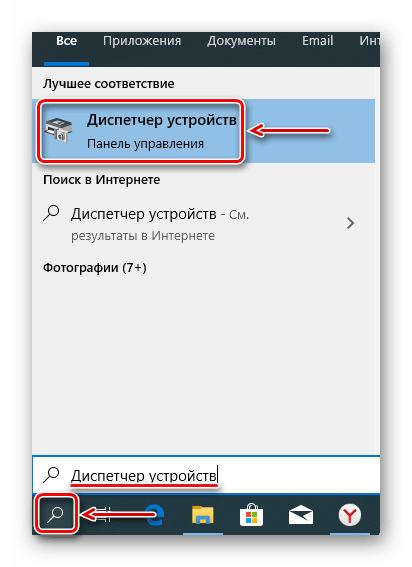
Зайдите в «Диспетчер устройств», чтобы проверить, включена ли ваша видеокарта. Сделать это можно, кликнув по кнопке «Пуск», чтобы написать в строке поиска «Диспетчер устройств» и нажать «Enter». В открывшемся окне отыщите свою графическую карту и двойным кликом по ней вызовете окно свойств.
Вкладка «Драйвер» будет содержать кнопку «Включить» – нажмите ее. Если кнопка неактивна, это говорит о том, что видеокарта уже включена.
Совет #5: Убедитесь, что блок питания компьютера работоспособен
Если вы решили расширить возможности своего компьютера, приобретя графический адаптер, узнайте, нуждается ли она в дополнительном питании, и в каком объеме. Питания от материнской платы таким мощным устройствам часто недостаточно, вот почему компьютер не видит новую видеокарту. Ее нужно подключить к блоку питания, но если ваше питающее устройство недостаточно мощное, ему не хватит ресурсов на обеспечение и материнской платы, и подключенной видеокарты. Лучше, если мощность блока питания будет немного превышать максимальное потребление энергии устройствами.
Совет #6: Удалите встроенный графический драйвер
Если наличие драйвера мешает определению выделенного аналога, нужно удалить неиспользуемое программное обеспечение. Наличие данных об интегрированном устройстве может быть всегда в приоритете для системы, кроме того новая графическая карта может быть неправильно обнаружена, вот почему после переустановки Windows компьютер не видит видеокарту. Что делать – войти в «Диспетчер устройств» и удалить драйвер интегрированного оборудования.
Совет #7: Попробуйте включить видеокарту через командную строку
Совет #8: Установите или обновите драйвер видеокарты
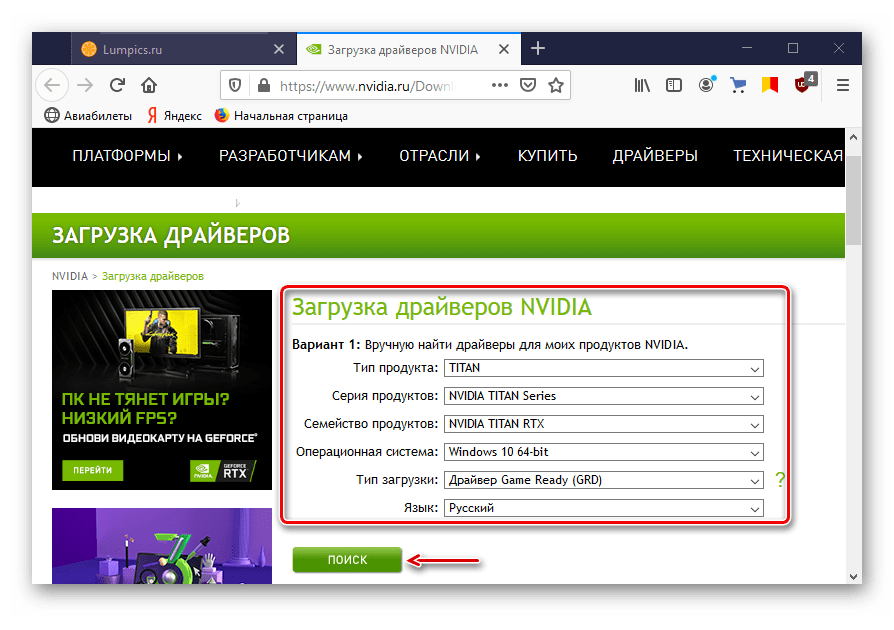
Купив выделенный графический процессор, устанавливайте только тот драйвер, который вы получили из официального источника. Если у вас его нет – загружайте с сайта производителя. Например, для устройства марки Nvidia программное обеспечение можно найти по адресу https://www.nvidia.com/Download/index.aspx. А свежую версию драйвера для компонентов производителя AMD Radeon вы найдете здесь: https://www.amd.com/en/support. С правильным программным обеспечением не возникнет вопрос, почему комп не видит видеокарту.
Как переустановить драйвер видеокарты Nvidia
Когда компьютер не видит видеокарту, но кулер работает, чаще всего виновато неправильно установленное или устаревшее программное обеспечение. Особенно это касается техники с Windows 10. Удалите все старые версии и установите новый драйвер.
Загружайте все компоненты только с официального сайта производителя. Запуская дистрибутив, не забудьте указать: «Свежая установка».
Как переустановить драйвер видеокарты AMD
Система начнет стирать данные, о состоянии процесса вас будет информировать строка состояния. Экран в это время может терять изображение, периодически становясь черным. В зависимости от производительности вашего ПК, процедура будет длиться до 10 минут.
Когда все файлы будут удалены, появится диалоговое окно, предлагающее перегрузить систему. Дайте согласие, потому что иначе процесс удаления окажется незавершенным. Нажатием кнопки «Restart Now» вы отправите компьютер в перезагрузку. Предварительно рекомендуется завершить работу всех открытых приложений.
Совет #9: Убедитесь, что проблема не в обновлении Windows
Что делать, если ПК не видит видеокарту, но она работает – убедиться, что в этом не виновата новая версия Windows. Иногда обновления, нацеленные на улучшения какого-то функционала, могут нарушать работу иных процессов. Если вы заметили, что видеокарта отказала сразу после установки нового релиза Windows, откатитесь к предыдущей версии. Чаще всего такая проблема встречается у Windows 10, которая в фоновом режиме загружает и устанавливает все компоненты обновлений, которые появляются в официальном источнике.
Если после отказа от конкретного пакета обновлений работоспособность видеокарты восстановилась, нужно будет поставить запрет на автоматическую повторную установку этих компонентов, чтобы больше не думать о том, почему компьютер не видит видеокарту в диспетчере устройств.
Совет #10: Проверьте кабель от монитора к видеокарте
Проверьте состояние кабеля, который соединяет монитор и системный блок. Вероятно, монитор не передает изображение вовсе не потому, что не работает видеокарта, а потому, что кабель поврежден, и сигнал по нему не поступает на устройство вывода графической информации. Мы не рекомендуем приобретать дешевые аналоги, чтобы не сомневаться в качестве продукта.
Совет #11: Обновите БИОС
BIOS, отвечая за связь всего подключенного оборудования к материнской плате, может наладить положение, когда видеокарта работает, но компьютер ее не видит. При этом достаточно обновить версию BIOS. Это поможет, когда возраст материнской платы и ее системы ввода-вывода мешает распознать свежее устройство.
Чтобы не вывести из рабочего состояния весь ПК, ищите новый BIOS только на сайте производителя своей материнской платы. И перед установкой ознакомьтесь со всеми возможными требованиями и рисками.
Совет #12: Установите видеокарту «по умолчанию»
Чтобы определить, почему ПК не видит видеокарту, исключите все программные причины. В том числе, установив ее в качестве устройства по умолчанию. Однако этот шаг вам будет доступен, если вы можете видеть свою видеокарту.
Вам станет доступен список программ, для которых вы сможете установить нужную видеокарту в качестве оборудования по умолчанию. Настроив, таким образом, одно из приложений, проверьте, работает ли с ним после этого видеокарта. Если все в порядке, установите ее как приоритетное оборудование и для остальных программных комплексов.
Заключительные советы
К сожалению, нередко приобретение выделенного графического процессора заканчивается тем, что вы пытаетесь выяснить, почему ноутбук не видит видеокарту. Не работает видеокарта на ноутбуке часто потому, что неисправен GPU BIOS. Это можно наладить, заменив прошивку компонента. В противном случае придется довольствоваться стандартом, который в состоянии передать VGA-интерфейс. Установить драйверы AMD или Nvidia в этом случае не удастся. Не имея опыта в вопросе смены прошивки, лучше обратиться за помощью к специалистам.
Если вы подозреваете в неисправности саму видеокарту, и при этом монитор не видит видеокарту, проверьте, как она работает в паре с другим компьютером. Если успеха не будет и с другим оборудованием, отдавайте видеокарту в сервис для выяснения причин. Возможно, специалисты выявят брак и заменят вам ее по гарантии.
Кроме неисправности видеокарты, проблемой может стать неработоспособный порт PCI-E x16, через который она подключается к материнской плате. Если при подключении к другому ПК графический процессор работает нормально, виноват, скорее всего, разъем, либо материнская плата не поддерживает такой тип подключаемого оборудования. Решением в таком случае будет замена устаревшей модели платы более новой. Если у вас есть вопросы, почему не отображается видеокарта, задайте их в комментариях, и мы поможем решить проблему, из-за которой видеокарта не видна в диспетчере устройств Windows.
BCDEdit /set
The BCDEdit /set command sets a boot entry option value in the Windows boot configuration data store (BCD). Use the BCDEdit /set command to configure specific boot entry elements, such as kernel debugger settings, memory options, or options that enable test-signed kernel-mode code or load alternate hardware abstraction layer (HAL) and kernel files. To remove a boot entry option, use the BCDEdit /deletevalue command.
Administrative privileges are required to use BCDEdit to modify BCD. Changing some boot entry options using the BCDEdit /set command could render your computer inoperable. As an alternative, use the System Configuration utility (MSConfig.exe) to change boot settings.
В Before setting BCDEdit options you might need to disable or suspend BitLocker and Secure Boot on the computer.
Alternatives to BCDEdit
Settings startup options
В To avoid the risk associated with using BCDEdit, consider using an alternative method to perform boot configuration discussed in this section.
Startup Settings
System Configuration Utility
Use the System Configuration Utility (MSConfig.exe) instead of BCDEdit when possible. For more information, see How to open MSConfig in Windows 10.
Syntax
Parameters
[ ]
The is the GUID that is associated with the boot entry. If you do not specify an , the command modifies the current operating system boot entry. If a boot entry is specified, the GUID associated with the boot entry must be enclosed in braces . To view the GUID identifiers for all of the active boot entries, use the bcdedit /enum command. The identifier for the current boot entry is . For more information about this option, use the following command: bcdedit /? ID
If you are using Windows PowerShell, you must use quotes around the boot entry identifier, for example: «<49916baf-0e08-11db-9af4-000bdbd316a0>« or «
Use the command line help to view options
Use the command line help for BCDEdit to display information available for a specific version of Windows.
The following sections describe some common datatypes and their associated values.
Boot Settings
bootlog [ yes | no ]
Enables the system initialization log. This log is stored in the Ntbtlog.txt file in the %WINDIR% directory. It includes a list of loaded and unloaded drivers in text format.
bootmenupolicy [ Legacy | Standard ]
Defines the type of boot menu the system will use. ForWindowsВ 10, WindowsВ 8.1, WindowsВ 8 and WindowsВ RT the default is Standard. For Windows ServerВ 2012В R2, Windows ServerВ 2012, the default is Legacy. When Legacy is selected, the Advanced options menu (F8) is available. When Standard is selected, the boot menu appears but only under certain conditions: for example, if there is a startup failure, if you are booting up from a repair disk or installation media, if you have configured multiple boot entries, or if you manually configured the computer to use Advanced startup. When Standard is selected, the F8 key is ignored during boot. WindowsВ 8 PCs start up quickly so there isn’t enough time to press F8. For more information, see Windows Startup Settings (including safe mode).
The option is available starting with WindowsВ 8 and Windows ServerВ 2012. You can also use the onetimeadvancedoptions to use the Advanced options (F8) menu (Legacy) one time on the next boot.
bootstatuspolicy policy
Controls the boot status policy. The boot status policy can be one of the following:
| Boot Status Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| DisplayAllFailures | Displays all errors if there is a failed boot, failed shutdown, or failed checkpoint. The computer will fail over to the Windows recovery environment on reboot. |
| IgnoreAllFailures | Ignore errors if there is a failed boot, failed shutdown, or failed checkpoint. The computer will attempt to boot normally after an error occurs. |
| IgnoreShutdownFailures | Only ignore errors if there is a failed shutdown. If there is a failed shutdown, the computer does not automatically fail over to the Windows recovery environment on reboot. This is the default setting for WindowsВ 8. |
| IgnoreBootFailures | Only ignore errors if there is a failed boot. If there is a failed boot, the computer does not automatically fail over to the Windows recovery environment on reboot. |
| IgnoreCheckpointFailures | Only ignore errors if there is a failed checkpoint. If there is a failed checkpoint, the computer does not automatically fail over to the Windows recovery environment on reboot. The option is available starting with WindowsВ 8 and Windows ServerВ 2012. |
| DisplayShutdownFailures | Displays errors if there is a failed shutdown. If there is a failed shutdown, the computer will fail over to the Windows recovery environment on reboot. Ignores boot failures and failed checkpoints. The option is available starting with WindowsВ 8 and Windows ServerВ 2012. |
| DisplayBootFailures | Displays errors if there is a failed boot. If there is a failed boot, the computer will fail over to the Windows recovery environment on reboot. Ignores shutdown failures and failed checkpoints. The option is available starting with WindowsВ 8 and Windows ServerВ 2012. |
| DisplayCheckpointFailures | Displays errors if there is a failed checkpoint. If there is a failed checkpoint, the computer will fail over to the Windows recovery environment on reboot. Ignores boot and shutdown failures. The option is available starting with WindowsВ 8 and Windows ServerВ 2012. |
quietboot [ on | off ]
Controls the display of a high-resolution bitmap in place of the Windows boot screen display and animation.
Do not use the quietboot option in WindowsВ 8 as it will prevent the display of bug check data in addition to all boot graphics.
sos [ on | off ]
Controls the display of the names of the drivers as they load during the boot process. Use sos on to display the names. Use sos off to suppress the display.
lastknowngood [ on | off ]
Enables boot to last known good configuration.
nocrashautoreboot [ on | off ]
Disables automatic restart on crash.
resumeobject (id)
Defines the identifier of the resume object that is associated with this operating system object.
safebootalternateshell [ on | off ]
Uses the alternate shell when booted into Safe mode.
winpe [ on | off ]
Enables the computer to boot to Windows PE.
onetimeadvancedoptions [ on | off ]
Controls whether the system boots to the legacy menu (F8 menu) on the next boot.
Display Settings
bootuxdisabled [ on | off ]
Disables boot graphics.
graphicsmodedisabled [ on | off ]
Indicates whether graphics mode is disabled and boot applications must use text mode display.
graphicsresolution
Defines the graphics resolution, 1024×768, 800×600,1024×600, etc.
highestmode [ on | off ]
Enables boot applications to use the highest graphical mode exposed by the firmware.
novga [ on | off ]
Disables the use of VGA modes entirely.
vga [ on | off ]
Forces the use of the VGA display driver.
Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) & KERNEL
hal file
Directs the operating system loader to load an alternate HAL file. The specified file must be located in the %SystemRoot%\system32 directory.
kernel file
Directs the operating system loader to load an alternate kernel. The specified file must be located in the %SystemRoot%\system32 directory.
Verification Settings
testsigning [ on | off ]
Controls whether WindowsВ 10, WindowsВ 8.1, WindowsВ 8, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, or Windows Vista will load any type of test-signed kernel-mode code. This option is not set by default, which means test-signed kernel-mode drivers on 64-bit versions of WindowsВ 10, WindowsВ 8.1, WindowsВ 8, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Vista will not load by default. After you run the BCDEdit command, restart the computer so that the change takes effect. For more information, see Introduction to Test-Signing
nointegritychecks [ on | off ] Disables integrity checks. Cannot be set when secure boot is enabled. This value is ignored by Windows 7 and WindowsВ 8.
disableelamdrivers [ yes | no ]
Controls the loading of Early Launch Antimalware (ELAM) drivers. The OS loader removes this entry for security reasons. This option can only be triggered by using the F8 menu. Someone must be physically present (at the computer) to trigger this option.
This option should only be used for debugging.
nx [Optin |OptOut | AlwaysOn |AlwaysOff]
Enables, disables, and configures Data Execution Prevention (DEP), a set of hardware and software technologies designed to prevent harmful code from running in protected memory locations. For information about DEP settings, see Data Execution Prevention.
| DEP Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Optin | Enables DEP only for operating system components, including the Windows kernel and drivers. Administrators can enable DEP on selected executable files by using the Application Compatibility Toolkit (ACT). |
| Optout | Enables DEP for the operating system and all processes, including the Windows kernel and drivers. However, administrators can disable DEP on selected executable files by using System in Control Panel. |
| AlwaysOn | Enables DEP for the operating system and all processes, including the Windows kernel and drivers. All attempts to disable DEP are ignored. |
| AlwaysOff | Disables DEP. Attempts to enable DEP selectively are ignored. On Windows Vista, this parameter also disables Physical Address Extension (PAE). This parameter does not disable PAE on Windows Server 2008. |
Processor Settings
groupsize maxsize
Sets the maximum number of logical processors in a single processor group, where maxsize is any power of 2 between 1 and 64 inclusive. By default, processor groups have a maximum size of 64 logical processors. You can use this boot configuration setting to override the size and makeup of a computer’s processor groups for testing purposes. Processor groups provide support for computers with greater than 64 logical processors. This boot option is available on 64-bit versions of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 and later versions. This boot option has no effect on the 32-bit versions of Windows 7.
Use the groupsize option if you want to force multiple groups and the computer has 64 or fewer active logical processors. For more information about using this option, see Boot Parameters to Test Drivers for Multiple Processor Group Support.
groupaware [ on | off ]
Forces drivers to be aware of multiple groups in a multiple processor group environment. Use this option to help expose cross-group incompatibilities in drivers and components. Processor groups provide support for computers with greater than 64 logical processors. This boot option is available on 64-bit versions of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 and later versions. This boot option has no effect on the 32-bit versions of Windows 7. You can use the groupaware option and the groupsize option to test driver compatibility to function with multiple groups when computer has 64 or fewer active logical processors.
The groupaware on setting ensures that processes are started in a group other than group 0. This increases the chances of cross-group interaction between drivers and components. The option also modifies the behavior of the legacy functions, KeSetTargetProcessorDpc, KeSetSystemAffinityThreadEx, and KeRevertToUserAffinityThreadEx, so that they always operate on the highest numbered group that contains active logical processors. Drivers that call any of these legacy functions should be changed to call their group-aware counterparts (KeSetTargetProcessorDpcEx, KeSetSystemGroupAffinityThread, and KeRevertToUserGroupAffinityThread).
maxgroup [ on | off ]
Maximizes the number of groups created in a processor group configuration. The maxgroup on setting assigns NUMA nodes to groups in a manner that maximizes the number of groups for a particular computer. The number of groups created is either the number of NUMA nodes the computer has, or the maximum number of groups supported by this version of Windows, whichever is smaller. The default behavior (maxgroup off) is to pack the NUMA nodes tightly into as few groups as possible.
Use the maxgroup option if you want to use multiple groups, the computer has 64 or fewer active logical processors, and the computer already has multiple NUMA nodes. This option can also be used to alter the default group configuration of a computer that has more than 64 logical processors.
Processor groups provide support for computers with greater than 64 logical processors. This option is available on 64-bit versions of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 and later versions. This boot option has no effect on the 32-bit versions of Windows 7.
onecpu [ on | off ]
Forces only the boot CPU to be used in a computer that has more than one logical processor. For example, the following command configures the current operating system loader to use one processor.
Memory Related Settings
increaseuserva Megabytes
Specifies the amount of memory, in megabytes, for user-mode virtual address space.
On 32-bit editions of Windows, applications have 4 gigabyte (GB) of virtual address space available. The virtual address space is divided so that 2 GB is available to the application and the other 2 GB is available only to the system.
The 4-gigabyte tuning feature, enabled with the increaseuserva option, allows you to increase the virtual address space that is available to the application up to 3 GB, which reduces the amount available to the system to between 1 and 2 GB. The BCEdit /set increaseuserva Megabytes command can specify any value between 2048 (2 GB) and 3072 (3 GB) megabytes in decimal notation. Windows uses the remaining address space (4 GB minus the specified amount) as its kernel-mode address space.
See 4-Gigabyte Tuning (Windows) for additional information about this feature.
nolowmem [ on | off ] Controls the use of low memory. When nolowmem on is specified, this option loads the operating system, device drivers, and all applications into addresses above the 4 GB boundary, and directs Windows to allocate all memory pools at addresses above the 4 GB boundary. Note that the nolowmem option is ignored in WindowsВ 8, Windows ServerВ 2012, and later versions of Windows.
pae [ Default | ForceEnable | ForceDisable ]
Enables or disables Physical Address Extension (PAE). When PAE is enabled, the system loads the PAE version of the Windows kernel.
On a computer that supports hardware-enabled Data Execution Prevention (DEP) and is running a 32-bit version of the Windows operating system that supports DEP, PAE is automatically enabled when DEP is enabled and, on all 32-bit versions of the Windows operating system, except Windows Server 2003 with SP1, PAE is disabled when you disable DEP. To enable PAE when DEP is disabled, you must enable PAE explicitly, by using /set nx AlwaysOff and /set pae ForceEnable. For more information about DEP, see Boot Parameters to Configure DEP and PAE.
For more information about using the pae parameter and the other parameters that affect PAE configuration, see Boot Parameters to Configure DEP and PAE.
removememory Megabytes
Removes memory from the total available memory that the operating system can use.
For example, the following command removes 256 MB of memory from the total available to the operating system associated with the specified boot entry.
truncatememory address Limits the amount of physical memory available to Windows. When you use this option, Windows ignores all memory at or above the specified physical address. Specify the address in bytes.
For example, the following command sets the physical address limit at 1 GB. You can specify the address in decimal (1073741824) or hexadecimal (0x40000000).
Additional Settings
disabledynamictick [ yes | no ]
Enables and disables dynamic timer tick feature.
This option should only be used for debugging.
forcelegacyplatform [ yes | no ]
Forces the OS to assume the presence of legacy PC devices like CMOS and keyboard controllers.
This option should only be used for debugging.
pciexpress [ default | forcedisable]
Enables or disables PCI Express functionality. If the computer platform supports the PCI Express features and the ACPI _OSC method grants control of the features to the operating system, Windows enables the advanced features through the PCI Express Native Control feature (this is the default). Use the forcedisable option to override the advanced PCI Express features and use legacy PCI Express behavior. For more information, see Enabling PCI Express Native Control in Windows.
tpmbootentropy [ default | ForceEnable | ForceDisable]
Determines whether entropy is gathered from the trusted platform module (TPM) to help seed the random number generator in the operating system.
tscsyncpolicy [ Default | Legacy | Enhanced ]
Controls the times stamp counter synchronization policy. This option should only be used for debugging.
usefirmwarepcisettings [ yes | no ]
Enables or disables the use of BIOS-configured peripheral component interconnect (PCI) resources.
useplatformclock [ yes | no ]
Forces the use of the platform clock as the system’s performance counter.
This option should only be used for debugging.
uselegacyapicmode [ yes | no ]
Used to force legacy APIC mode, even if the processors and chipset support extended APIC mode.
useplatformtick [ yes | no ]
Forces the clock to be backed by a platform source, no synthetic timers are allowed. The option is available starting in WindowsВ 8 and Windows ServerВ 2012.
This option should only be used for debugging.
xsavedisable [ 0 | 1 ]
When set to a value other than zero (0), disables XSAVE processor functionality in the kernel.
x2apicpolicy [ enable | disable ]
Enables or disables the use of extended APIC mode, if supported. The system defaults to using extended APIC mode if it is available.
Debugger Settings
To work with the debugger settings, use the following commands.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| BCDEdit /bootdebug | The /bootdebug boot option enables or disables boot debugging of the current or specified Windows operating system boot entry. |
| BCDEdit /dbgsettings | The /dbgsettings option sets or displays the current global debugger settings for the computer. To enable or disable the kernel debugger, use the BCDEdit /debug option. |
| BCDEdit /debug | The /debug boot option enables or disables kernel debugging of the Windows operating system associated with the specified boot entry or the current boot entry. |
Hypervisor Debugger Settings
Use the BCDEdit / hypervisorsettings option to set or display the hypervisor debugger settings for the system. For more information, see BCDEdit /hypervisorsettings.
hypervisordebug [ On | Off ]
Controls whether the hypervisor debugger is enabled.
Hypervisor Settings
hypervisoriommupolicy [ default | enable | disable]
Controls whether the hypervisor uses an Input Output Memory Management Unit (IOMMU).
hypervisorlaunchtype [ Off | Auto ]
Controls the hypervisor launch options. If you are setting up a debugger to debug Hyper-V on a target computer, set this option to Auto on the target computer. For more information, see Create a Virtual Machine with Hyper-V.
hypervisorloadoptions NOFORCESNOOP [ Yes | No ]
Specifies whether the hypervisor should enforce snoop control on system IOMMUs.
hypervisornumproc number
Specifies the total number of logical processors that can be started in the hypervisor.
hypervisorrootproc number
Specifies the maximum number of virtual processors in the root partition and limits the number of post-split Non-Uniform Memory Architecture (NUMA) nodes which can have logical processors started in the hypervisor.
hypervisorrootprocpernode number
Specifies the total number of virtual processors in the root partition that can be started within a pre-split Non-Uniform Memory Architecture (NUMA) node.
hypervisoruselargevtlb [ yes | no]
Increases virtual Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) size.
Emergency Management Services
The BCDEdit /ems option enables or disables Emergency Management Services (EMS) for the specified operating system boot entry. For more information, see BCDEdit /ems.
The BCDEdit /emssettings option sets the global Emergency Management Services (EMS) settings for the computer. For more information, see For more information, see BCDEdit /emssettings.
Event Logging
The BCDEdit /event command enables or disables the remote event logging for the specified boot entry. For more information, see BCDEdit /event.
Comments
For more information about specific BCD elements and boot options, you can use the commands BCDEdit /? OSLOADER and BCDEdit /? TYPES OSLOADER.
To view the current boot entries and their settings, use the bcdedit /enum command. This command displays the active boot entries and their associated globally unique identifiers (GUID). Use the identifiers with the /set command to configure options for a specific boot entry.
To delete a boot option value that you have set, use the /deletevalue option. The syntax for the command is as follows:
bcdedit /deletevalue [ ] datatatype
For example, if you change the processor group option, groupsize, to a new value for testing purposes, you can revert to the default value of 64 by typing the following command and then restarting the computer.
Any change to a boot option requires a restart to take effect. For information about commonly used BCDEdit commands, see Boot Configuration Data Editor Frequently Asked Questions.
DTrace
DTrace (DTrace.exe) is a command-line tool that displays system information and events. There is a bcedit option to enable dtrace. For information about the DTrace BCDEdit options available, see the installing section of DTrace on Windows.
Requirements
Minimum supported client: WindowsВ Vista
Minimum supported server: Windows ServerВ 2008